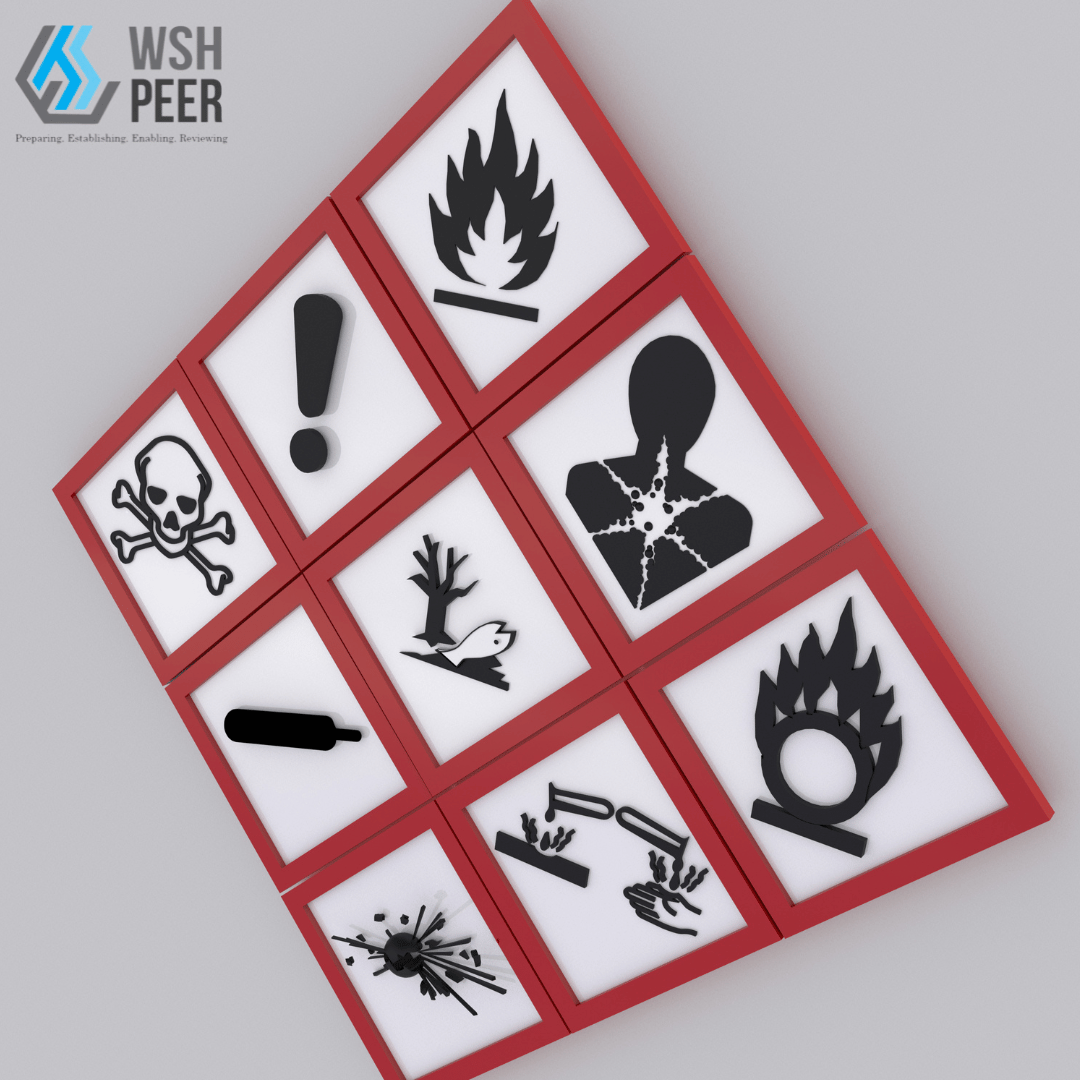
In industrial environments, construction and maintenance often require work in confined spaces, which can be hazardous and lead to sudden, fatal incidents. Workers might underestimate the risks of entering restricted areas or oxygen-depleted environments, sometimes with tragic outcomes. For instance, simply looking into a nitrogen-filled tank can cause unconsciousness within 15-20 seconds and death in 2-4 minutes.
What is a Confined Space?
A confined space refers to any chamber, tank, manhole, vat, silo, pit, pipe, flue, or other enclosed area where dangerous gases, vapors, or fumes are present to a degree that poses a risk of fire, explosion, or asphyxiation; where the air supply is inadequate or likely to become inadequate for sustaining life; or where there is a risk of engulfment by materials (Singapore Workplace Safety And Health Act).
The examples are include:
- Tanks and Vessels: These are designed to hold liquids or gases and require inspection and maintenance.
- Pasteurizing Machines: In the brewing industry, these machines use hot steam and need to be shut down and cooled for maintenance.
- Tunnels and Pits: These are often found below ground level and house piping and cables.
Confined spaces must be clearly identified, with visible danger signs and barriers to prevent unauthorized entry. When designing a plant, avoiding confined space entry is ideal. Consider alternatives like easy disassembly of equipment, adequate space for entry and exit, and special tools.
Employers need to develop a written procedure for confined space entry, accessible and understandable to all workers. Training is crucial and can be part of site induction for contractors or a structured program for employees.
Components of a Confined Space Permit Procedure
Letter of Appointment
The Letter of Appointment formally designates the individuals authorized to oversee and perform work in confined spaces. It specifies their responsibilities and ensures they are adequately trained and competent for the task. This document is crucial for accountability and ensuring that only qualified personnel are involved in confined space operations.
Safe Work Procedure
The Safe Work Procedure outlines the step-by-step process for safely conducting work in confined spaces. It includes detailed instructions on how to prepare for entry, perform the work, and safely exit the space. This procedure is designed to minimize risks and ensure that all safety protocols are followed meticulously.
Risk Assessment
A comprehensive Risk Assessment identifies all potential hazards associated with confined space work. This assessment evaluates the likelihood and severity of each hazard, like Isolate energy sources, purge with air, maintain oxygen levels, and test for toxic or explosive gases providing a clear understanding of the risks involved. It is a critical tool for planning and implementing effective control measures to protect workers.
The Confined Space Rescue Plan details the procedures for rescuing individuals in the event of an emergency. It includes the roles and responsibilities of the rescue team, the equipment required, and the steps to be taken to ensure a swift and safe rescue. This plan is essential for minimizing the impact of any incident that may occur.
Toolbox Meeting
Before any confined space work begins, a Toolbox Meeting is held to brief all workers on the task, potential hazards, and safety measures. This meeting ensures that everyone is aware of their responsibilities and understands the procedures to be followed. It also provides an opportunity to address any concerns or questions.
The Confined Space Entry/Work Operation Checklist is a detailed list of tasks and safety checks that must be completed before, during, and after work in a confined space. This checklist ensures that all necessary precautions are taken and that no steps are overlooked, promoting a systematic and thorough approach to safety.
The Confined Space Entry and Exit Log is a record of all personnel entering and exiting the confined space. This log includes the time of entry and exit, the purpose of the entry, and any observations or incidents. Maintaining this log is crucial for tracking personnel movements and ensuring accountability during confined space operations.
Conclusion
Working in confined spaces in industrial settings is very dangerous. Risks include getting trapped, running out of air, being exposed to harmful chemicals, and falling debris. To reduce these dangers, it’s crucial to follow strict safety procedures. A confined space permit system includes several key components. help ensure that safety protocols are clear and followed. Regularly reviewing and improving these procedures keeps workers safe by addressing new risks as they arise.
For better management of workplace safety, consider using solutions like PEER which provides tools to help manage and monitor safety protocols, making confined space work safer and more efficient. Using such solutions can greatly enhance safety and compliance in confined space operations, protecting workers and preventing accidents.